In today’s highly connected and digitized world, businesses face an increasing number of security threats that can compromise their sensitive data and cause severe financial and reputational damage. In fact, Cisco data estimates that distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks (a form of cybercrime) will grow to 15.4 million by 2023, more than double the 7.9 million in 2018.
As businesses continue to adopt new technologies and expand their digital footprint, it has become more critical than ever to implement robust security measures to safeguard their assets and protect against potential cyber threats. Microsoft Dynamics 365 Finance and Operations serve as the backbone of many businesses’ operations. It is a holistic system that requires user security to protect sensitive data and can handle everything from financial transactions to customer data and supply chain management.
This blog will explore user management, access controls, and permission management, along with available security features and best practices. By implementing the right security measures, you can ensure your F&O environment is secure and your data is protected.
1. Security Architecture in F&O
Having a solid grasp of the security architecture of Dynamics 365 Finance and Operations is key to tailoring security measures to meet your business needs. The diagram below offers a bird’s-eye view of the security architecture, providing a foundation for better understanding and customizing security settings.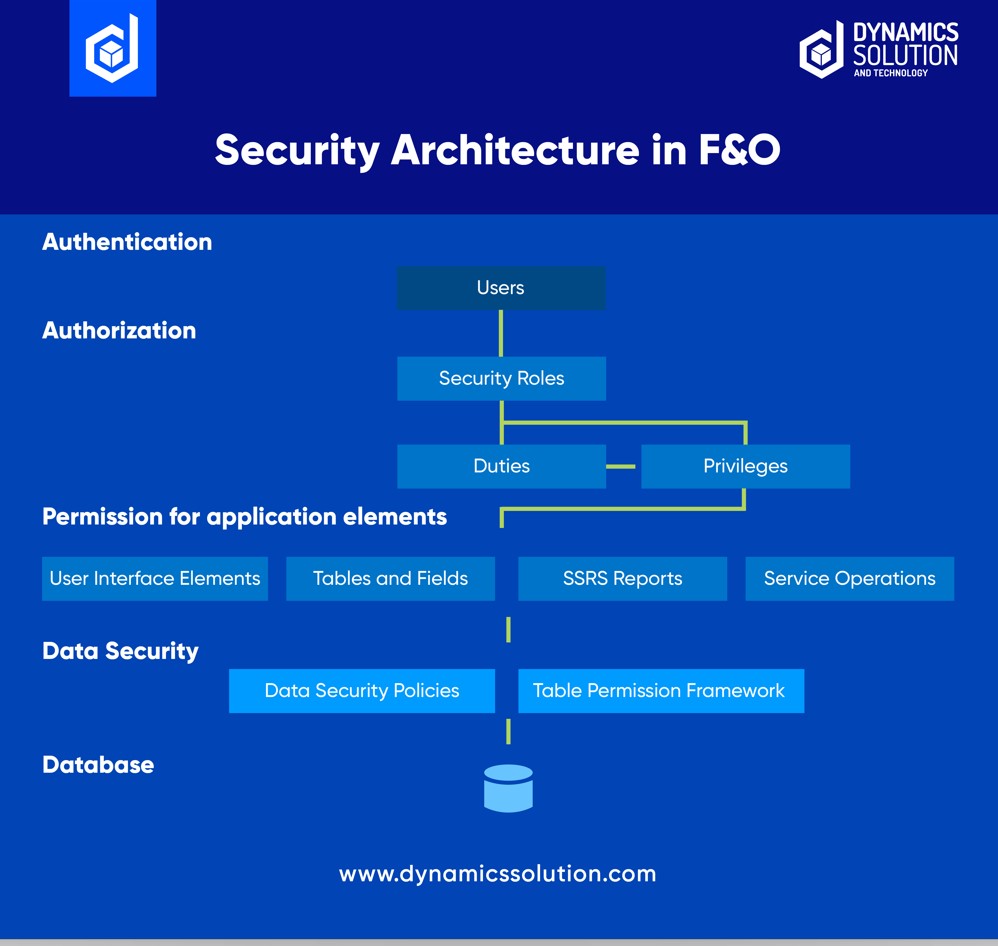
1.1 Authentication
To connect to Finance and Operations, users must be authenticated and have user rights. Microsoft Azure Active Directory is the primary identity provider. Users require a valid AAD (Azure Active Directory) account in an authorized tenant and must be provisioned into a Finance and Operations instance by default.
1.2 Authorization
In Finance and Operations, authorization controls program access. Security permissions are utilized to regulate access to specific program elements such as menus, menu items, reports, web controls, and fields. This ensures that users can only access the program elements they have authorization to use.
1.3 Data Security
Access to program elements is granted through authorization, while data security is used to prevent access to tables, fields, and rows in the database.
To regulate access to transactional data, you can assign data security policies to security roles using the extensible data security framework. These policies can restrict access to data based on factors such as the effective date or user data, like sales territory or organization.
Record-level security, previously used for securing data in Dynamics AX 2012 and earlier versions, is now obsolete. Extensible data security is the preferred method for securing or filtering data in the program.
1.4 Auditing
Auditing of user sign-in and sign-out is now enabled in Finance and Operations. The system logs when a user signs in or out of the application. A sign-out is logged even if the user’s session expires or ends.
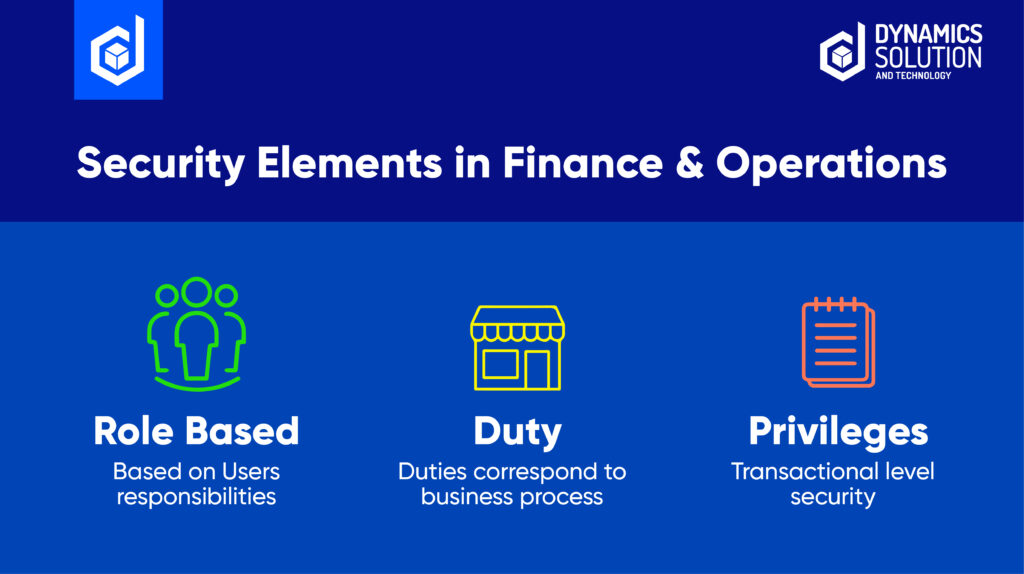
Elements of Security in Dynamics 365 Finance & Operations
2.1 Roles
Security roles are collections of privileges and duties that allow users (assigned to them) access to various program elements, including menus, forms, reports, and buttons. These elements are referred to as “securable objects“.
The purpose of security roles is to provide users in a specific organizational role with all the security required to conduct their daily tasks and operations. Dynamics 365 Finance and Operations comes with 137 preconfigured security roles.
In D365 users are assigned to security roles based on their responsibilities in the business process and organization.
Security roles fall into a hierarchical model with security roles and the top followed by duties, privileges and then the securable objects that are accessed by the security model. Below is an illustration of the Dynamics 365 Finance and Operations security model.
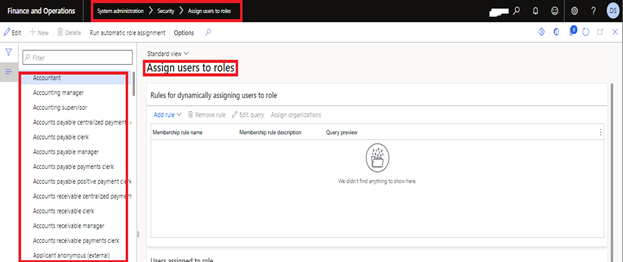
To assign users to roles you can follow this path attached in the snapshot.
2.2 Duty
In the security model, duties are below security roles and security roles are made up of one or many duties. Duties are a collection of security privileges and typically represent a specific part or piece of a business process. You will see duties like “Maintain customer data,” “Inquire about accounting data,” or “Generating financial reports”. Adding or removing duties is the most common way to grant or revoke access to certain parts of a business process.
Typically, the system administrator will only add or remove privileges when there is a unique or very granular security requirement that must be fulfilled.
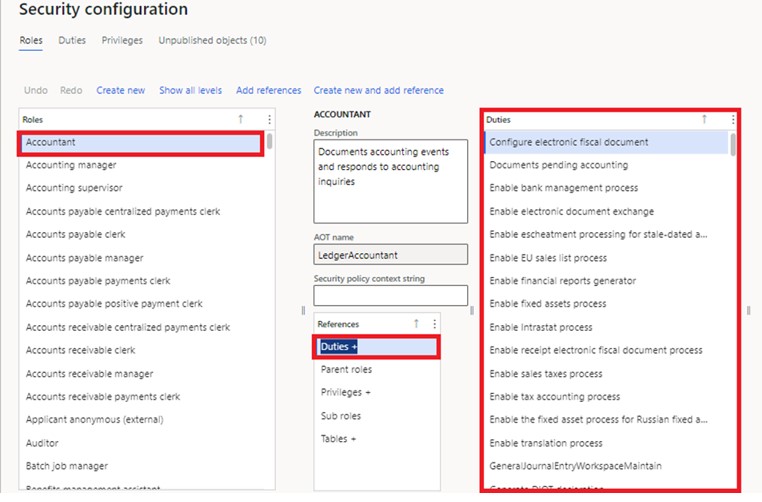
To access the duties, follow the following path.
System administration > security > security configuration
2.3 Privilege
The security privilege is the lowest level in the Dynamics 365 Finance and Operations security model. The security privilege contains the Create, Read, Update, Delete (CRUD) level permissions that can be toggled to meet very granular security requirements. Although security privileges can be added directly to a security role to meet a specific security requirement, it is best practice to assign it to a duty. Security privileges are the gateway to all access to any securable object in the application.
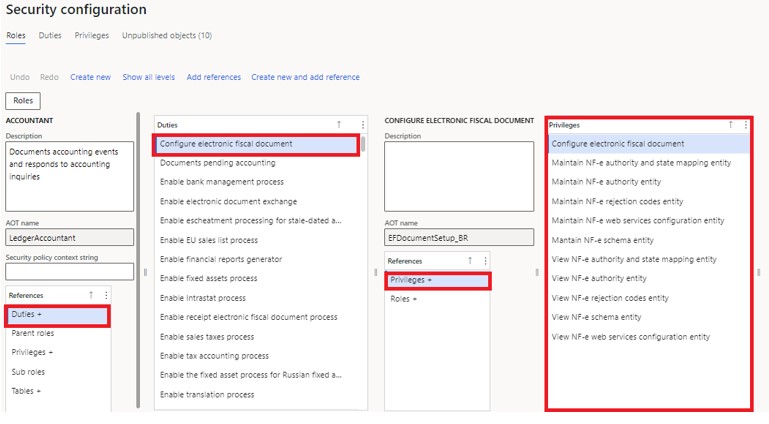
So, from the above screenshot, you can have an idea of how a duty can have different privileges in it.
Security management is a detailed implementation plan and requires the users to set up all the components and elements beforehand. After the initiation, they can move on to the step-by-step implementation phase in the next blog.
Nevertheless, organizations desire a seamless implementation process, and collaborating with an experienced Microsoft implementation partner is full of strengths. Dynamics Solution and Technology offer improved efficiency levels, experienced personnel, and a customer-centric approach to ensure swift deployment with a promise of data security and data management along the way.
Stay tuned for the next blog providing a thorough insight into the implementation of Guide to Dynamics 365 Finance and Operations Security Management!







